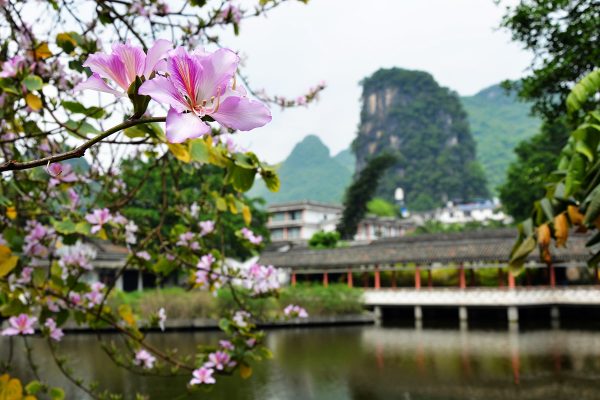
Yangshuo is a small town tucked away in the Karst Mountains of Guangxi, yet it has become something of an anomaly in China. By ratio, Yangshuo boasts one of the largest populations of English speaking Chinese people and foreign expats in the whole country. As a matter of fact, some locals say it even rivals Beijing and Shanghai as an international hub. Nestled amongst the verdant mountains and beside the rippling waters of the Li River, Yangshuo is undoubtedly one of the most beautiful places in Guangxi. It is an ideal place to start any tour of China, since the abundance of English speakers and balanced mixture of Western and Eastern influences makes it an easy introduction to the country.
The name “Yangshuo” derives from the Chinese words “yang” (阳) and “shuo” (朔). “Yang” is the well-known antagonist to “yin” in Taoist philosophy and symbolises positivity, masculinity and light. “Shuo” means “new moon” in Chinese, so the implication is that, night or day, Yangshuo is one of the brightest places on earth. Considering how modern Yangshuo has become, the town has a history that stretches back over 1,000 years. It was founded in 265 A.D., during the Jin Dynasty (265-420), and in 590, during the Sui Dynasty (581-618), the county seat was moved from Xingping to Yangshuo. It has remained the county town ever since, although it is still under the administrative control of Guilin city.
On top of the resident expat population, there is also a substantial constituency of native ethnic minorities, such as the Yao, Hui, Zhuang, and Miao people. This ethnic diversity means that the souvenirs, performances and cuisine on offer in Yangshuo are particularly varied. Stalls featuring Tibetan silver, Dong embroidered cloth, and Miao batik abound throughout the streets of Yangshuo. These little handcrafted trinkets make perfect souvenirs or mementos. There are two main tourist streets, known as West Street and Diecuilu, and they boast the majority of the souvenir stalls. Since the town is located deep within the countryside, there are also numerous fruit and vegetable farms in the vicinity. As you walk down the streets of Yangshuo, you’ll be met with a plethora of fresh fruits you may have never tried before, such as mouth-watering mangosteens, dubious smelling durian, and tantalising persimmons.

Yangshuo was first put on the map by Lonely Island in 1980 when they featured it in their travel guide. Since then, it has remained incredibly popular with foreign and domestic tourists alike. The landscape in Yangshuo has become so popular that it even featured in the movie Star Wars Episode III: Revenge of the Sith as Chewbacca’s home planet of Kashyyyk and also featured as a level in the landmark 1993 video game Doom. The image of the Li River on the 20 yuan note is also very close to Yangshuo and so, if you don’t fancy taking the long cruise from Guilin to Yangshuo, travelling directly to Yangshuo to visit the site is far quicker.
Not only is Yangshuo a perfect place to tour the Karst Mountains and the Li River, it is also a popular cycling and rock-climbing destination. As few public buses travel into the countryside, cycling is the ideal method of exploring Yangshuo County and visiting several of the tourist attractions, such as Moon Hill and Big Banyan. You can hire mountain bikes in the town centre for between 20 to 70 yuan (£2 to £7) per day depending on the condition of the bicycle. If you opt for one of the cheaper bicycles, we recommend you check the brakes and suspension before you agree to rent it.
In 1992, American rock climber Todd Skinner first popularised Yangshuo when he pioneered a number of the now established climbing routes, including the “Moonwalker” on the arch of Moon Hill. Nowadays there are plenty of tourist services in Yangshuo that focus exclusively on rock climbing and, with over 200 climbing routes in the vicinity, you’ll be spoilt for choice! Low Mountain, Twin Gates, Baby Frog, The Egg, Bamboo Grove and Wine Bottle Cliff are just a few examples of the scenic climbing spots on offer.
 Thanks to the Western expats now living in Yangshuo, the town boasts a variety of Western-style restaurants, cafés and bars that you won’t find in other Chinese towns. The food on offer in most of these restaurants is of a good standard and can provide a much needed rest from Chinese food if you’ve been travelling around the country for too long. Although most places close around 2am, Yangshuo boasts some of the most exciting nightlife in Guangxi. Many hostels will have their own bars and, coupled with the established bars and nightclubs in the town, this makes for a lively and unique atmosphere in the evenings. These hostel bars provide a wonderful opportunity to meet other travellers and backpackers on your journey.
Thanks to the Western expats now living in Yangshuo, the town boasts a variety of Western-style restaurants, cafés and bars that you won’t find in other Chinese towns. The food on offer in most of these restaurants is of a good standard and can provide a much needed rest from Chinese food if you’ve been travelling around the country for too long. Although most places close around 2am, Yangshuo boasts some of the most exciting nightlife in Guangxi. Many hostels will have their own bars and, coupled with the established bars and nightclubs in the town, this makes for a lively and unique atmosphere in the evenings. These hostel bars provide a wonderful opportunity to meet other travellers and backpackers on your journey.
Since the town has been geared up for tourism, there are plenty of hostels and hotels in Yangshuo. Prices and standards can range greatly between them, so we recommend doing some research before you book one. In spite of its popularity with foreign tourists, Yangshuo is not the easiest place to get to. There is no airport or train station in Yangshuo, so you must travel there either by bus or by boat. A boat cruise from Guilin to Yangshuo can take upwards of 4 to 5 hours and is quite expensive, but is worth it for the spectacular views along the Li River. Otherwise, express buses run from Guilin Bus Station to Yangshuo every 10 to 20 minutes and take just under an hour. There are also buses running from Guilin Train Station to Yangshuo every 5 to 10 minutes but these take just under 2 hours.













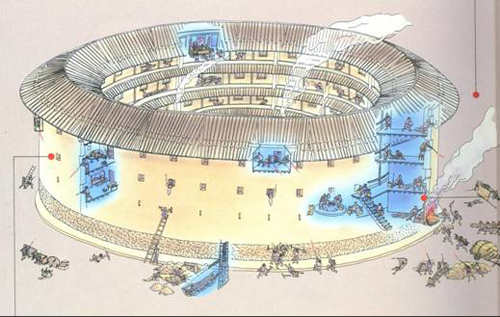


 Huiyuan Lou was built in 1909 and is a typical example of a Tulou that follows the “connected rooms” design. Because of its short history, the whole building is well preserved and thus serves as a good example of what a circular Tulou should look like.
Huiyuan Lou was built in 1909 and is a typical example of a Tulou that follows the “connected rooms” design. Because of its short history, the whole building is well preserved and thus serves as a good example of what a circular Tulou should look like.

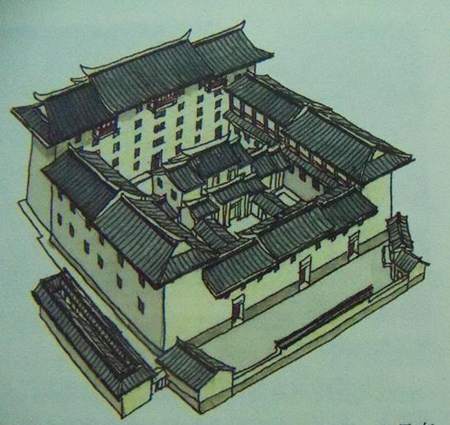
 Hegui Lou is a very typical rectangular Tulou. It was built in 1732 and follows the “connected rooms” design. Hegui lou was originally four-storeys high. In 1864 it was destroyed by robbers during an attack, and it was subsequently rebuilt as a five-storey Tulou. The main structure of the new compound follows that of a rectangular Tulou and it has 24 rooms on each of its five floors. A hall in the yard is connected to the Ancestral Hall in the main building. There is also now a front yard to provide more space for residents.
Hegui Lou is a very typical rectangular Tulou. It was built in 1732 and follows the “connected rooms” design. Hegui lou was originally four-storeys high. In 1864 it was destroyed by robbers during an attack, and it was subsequently rebuilt as a five-storey Tulou. The main structure of the new compound follows that of a rectangular Tulou and it has 24 rooms on each of its five floors. A hall in the yard is connected to the Ancestral Hall in the main building. There is also now a front yard to provide more space for residents.
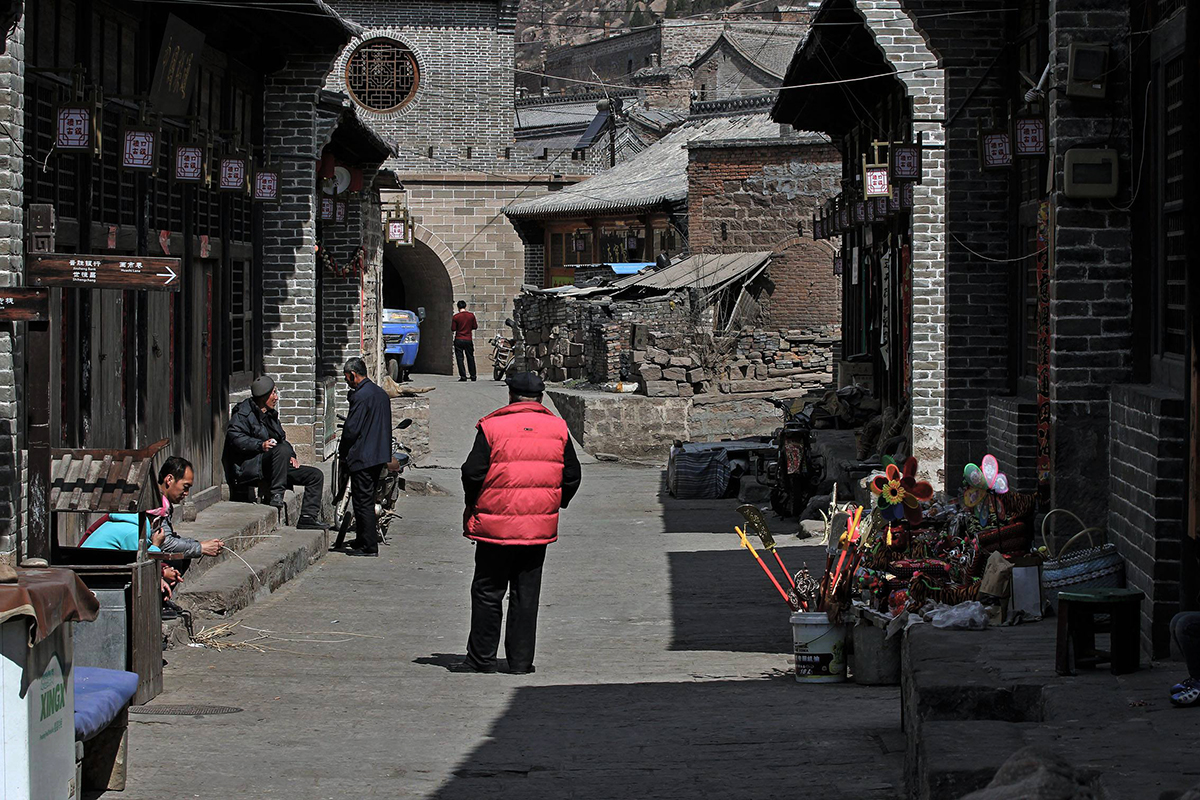



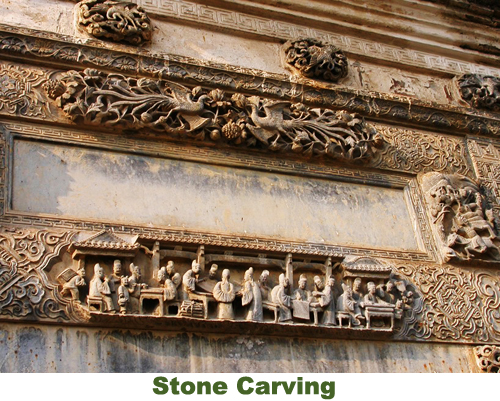
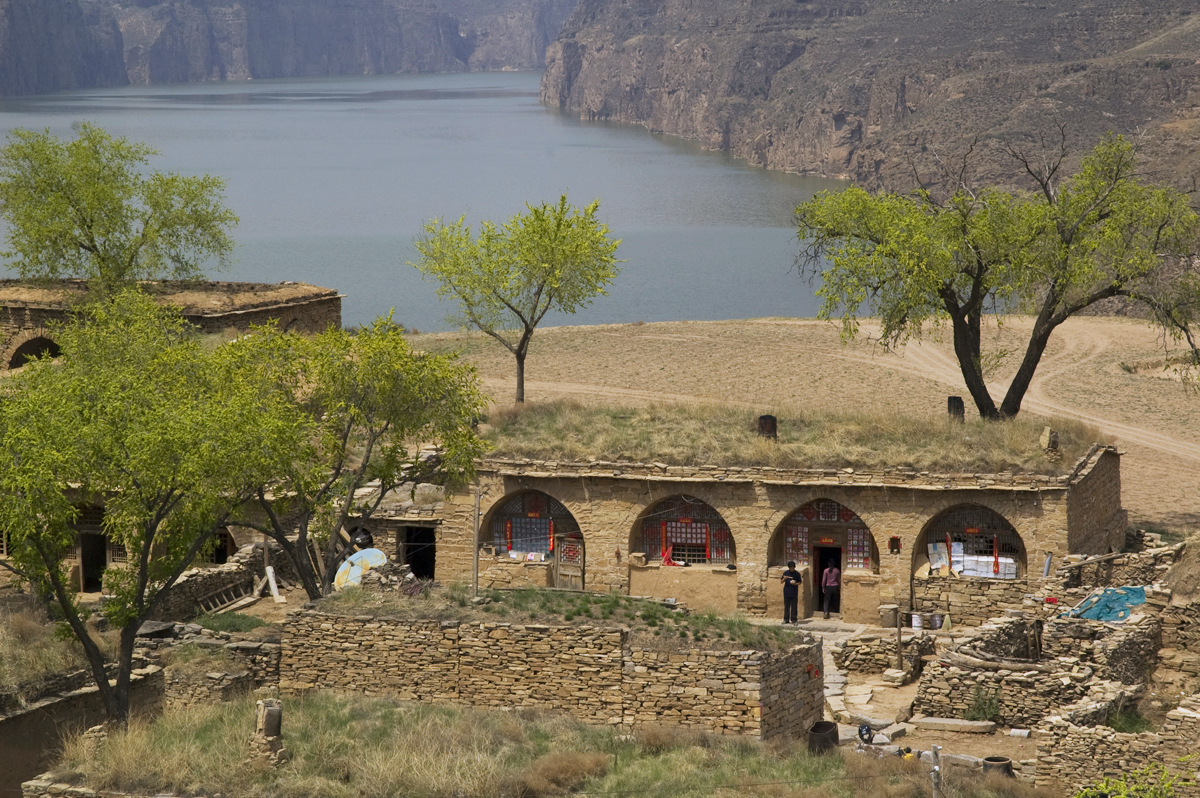
 Although it may no longer be the glorious trade port it once was, Qikou is still a picturesque ancient town with many historic buildings that have been beautifully preserved. In order to protect them from flooding, many of these houses, known as “yaodongs” or “loess cave houses,” have been physically carved into the steep hillside along the banks of the Yellow River. Looming over these houses on a raised platform, the Black Dragon Temple is the ideal place to enjoy a panoramic view of town. The temple is dedicated primarily to two separate deities: the legendary Black Dragon; and Guan Yu, a military general from the Three Kingdoms Period (220-280) who was eventually deified.
Although it may no longer be the glorious trade port it once was, Qikou is still a picturesque ancient town with many historic buildings that have been beautifully preserved. In order to protect them from flooding, many of these houses, known as “yaodongs” or “loess cave houses,” have been physically carved into the steep hillside along the banks of the Yellow River. Looming over these houses on a raised platform, the Black Dragon Temple is the ideal place to enjoy a panoramic view of town. The temple is dedicated primarily to two separate deities: the legendary Black Dragon; and Guan Yu, a military general from the Three Kingdoms Period (220-280) who was eventually deified.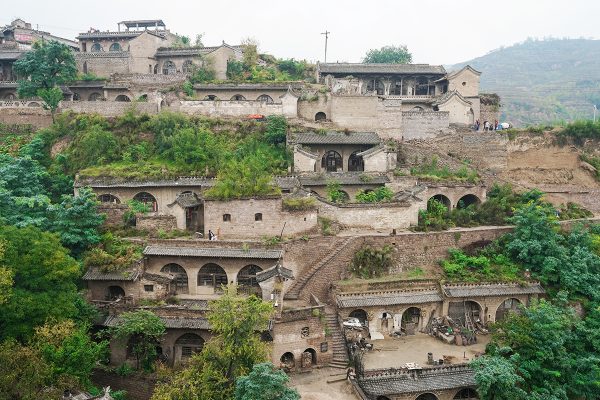


 Once you’ve passed through the first three entrances of the temple, you’ll arrive at the magnificent Baolun Hall. It was originally built in 1542, during the Ming Dynasty, and is famed for its stunning murals, which have barely faded in spite of the fact that they are over 500 years old! Vivid sculptures of lions, clouds, and lotuses grace the façades of bluestone parapets, wooden eaves, and crossbeams. Ascending the wooden staircase to the attic, you’ll be treated with a breath-taking panoramic view of the village below and the lofty Mount Huang in the distance.
Once you’ve passed through the first three entrances of the temple, you’ll arrive at the magnificent Baolun Hall. It was originally built in 1542, during the Ming Dynasty, and is famed for its stunning murals, which have barely faded in spite of the fact that they are over 500 years old! Vivid sculptures of lions, clouds, and lotuses grace the façades of bluestone parapets, wooden eaves, and crossbeams. Ascending the wooden staircase to the attic, you’ll be treated with a breath-taking panoramic view of the village below and the lofty Mount Huang in the distance.



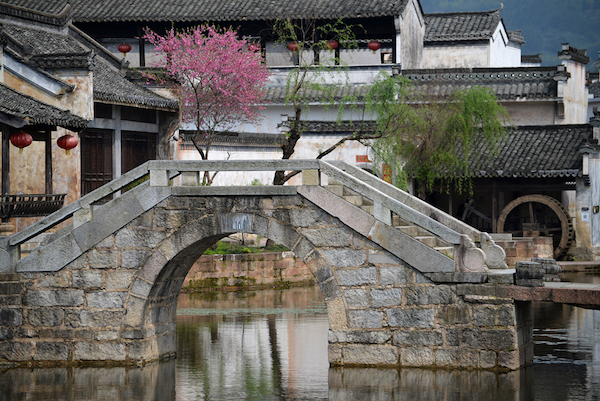
 The outer wall of the compound is known as a “horse-head wall”, because it was said to resemble a horse’s head in shape. These high, crenelated walls were designed to separate Hui residences from each other, in order to prevent the spread of fire, to block out cold drafts, and to deter thieves. The roofs of all the buildings are constructed so that they incline towards the inner courtyard. Since the Hui merchants believed that water was a symbol of wealth, having all rainwater trickle into the inner courtyard symbolised the flow of wealth into the family. The rainwater would then collect in a large jar at the centre of the courtyard, which could be used in the event of a fire. Like true businessmen, the Hui merchant families never missed a trick!
The outer wall of the compound is known as a “horse-head wall”, because it was said to resemble a horse’s head in shape. These high, crenelated walls were designed to separate Hui residences from each other, in order to prevent the spread of fire, to block out cold drafts, and to deter thieves. The roofs of all the buildings are constructed so that they incline towards the inner courtyard. Since the Hui merchants believed that water was a symbol of wealth, having all rainwater trickle into the inner courtyard symbolised the flow of wealth into the family. The rainwater would then collect in a large jar at the centre of the courtyard, which could be used in the event of a fire. Like true businessmen, the Hui merchant families never missed a trick!

